Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Calcium & Bone Metabolism
- Review and Update of the Risk Factors and Prevention of Antiresorptive-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw
- Ha Young Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(5):917-927. Published online October 21, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1170

- 4,501 View
- 269 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Antiresorptive-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (ARONJ) is a rare but serious adverse event of bisphosphonate or denosumab administration; it is associated with severe pain and a deteriorated quality of life. Since its first report in 2003, there have been many studies on its definition, epidemiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Nevertheless, the epidemiology and mechanisms underlying this condition have not yet been fully delineated and several risk factors are known. Moreover, as there is no effective treatment currently available for osteonecrosis of the jaw, prevention is essential. Furthermore, close cooperation between prescribing physicians and dentists is important. The aim of this review was to provide up-to-date information regarding the risk factors and prevention of ARONJ from a physician’s perspective.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk factors for dental findings of the development of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: Investigation of 3734 teeth in cancer patients receiving high dose antiresorptive agents
Mitsunobu Otsuru, Yoshinari Fujiki, Sakiko Soutome, Norio Nakamura, Taro Miyoshi, Tomofumi Naruse, Mizuho Ohnuma, Yuka Hotokezaka, Satoshi Rokutanda, Masahiro Umeda
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(1): 203. CrossRef - Editorial: Immunological processes in maxillofacial bone pathology
Matthias Tröltzsch
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Polysacharide of Agaricus blazei gel mitigates bone necrosis in model of the jaws related to bisphosphonate via Wnt signaling
Vanessa Costa de Sousa, Fátima Regina Nunes Sousa, Raquel Felipe Vasconcelos, Gisele Angelino Barreto, Conceição S. Martins, Nilson Romero Dias, Sislana Costa, Maria Jennifer Chaves Bernardino, George de Almeida Silva, Nadine Linhares, Delane Gondim, Mirn
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevention of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw after tooth extraction by local administration of antibiotics and atelocollagen sponge: A preliminary study
Natsumi Nakamura, Sakiko Soutome, Akira Imakiire, Satoshi Rokutanda, Seigo Ohba, Shunsuke Sawada, Yuka Kojima, Yuki Sakamoto, Yoshiko Yamamura, Madoka Funahara, Mitsunobu Otsuru, Masahiro Umeda
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - When and how to stop denosumab therapy in a patient with osteoporosis
Eirena L. Goulden, Rachel K. Crowley
Clinical Endocrinology.2023; 98(5): 649. CrossRef - Clinical and Histopathological Aspects of MRONJ in Cancer Patients
George Adrian Ciobanu, Laurențiu Mogoantă, Adrian Camen, Mihaela Ionescu, Daniel Vlad, Ionela Elisabeta Staicu, Cristina Maria Munteanu, Mircea Ionuț Gheorghiță, Răzvan Mercuț, Elena Claudia Sin, Sanda Mihaela Popescu
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(10): 3383. CrossRef - Bisphosphonates and osteonecrosis of the jaws: Clinical and forensic aspects
Diana Nogueira, Inês Morais Caldas, Ricardo Jorge Dinis-Oliveira
Archives of Oral Biology.2023; 155: 105792. CrossRef - Correlations between Immune Response and Etiopathogenic Factors of Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw in Cancer Patients Treated with Zoledronic Acid
George Adrian Ciobanu, Laurențiu Mogoantă, Sanda Mihaela Popescu, Mihaela Ionescu, Cristina Maria Munteanu, Ionela Elisabeta Staicu, Răzvan Mercuț, Cristian Corneliu Georgescu, Monica Scrieciu, Daniel Vlad, Adrian Camen
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(18): 14345. CrossRef - Analysis of the Degree of Information of Dental Surgeons about Antiresorptive Drugs According to the Time Since Graduation in Dentistry
Flávia Godinho Costa Wanderley Rocha, Roberto Paulo Correia de Araújo
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Safety and Efficacy of Pamidronate in Neonatal Hypercalcemia Caused by Subcutaneous Fat Necrosis: A Case Report
Stefano Martinelli, Marco Pitea, Italo Francesco Gatelli, Tara Raouf, Graziano Barera, Ottavio Vitelli
Frontiers in Pediatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Zoledronic acid for osteoporosis and associated low-energy fractures
S. S. Rodionova, A. F. Kolondaev, A. N. Torgashin, I. A. Solomyannik
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2022; (21): 163. CrossRef
- Risk factors for dental findings of the development of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: Investigation of 3734 teeth in cancer patients receiving high dose antiresorptive agents

- Clinical Study
- Effects of Systemic Glucocorticoid Use on Fracture Risk: A Population-Based Study
- Ji Weon Koh, Junkang Kim, Hyemin Cho, Yong-Chan Ha, Tae-Young Kim, Young-Kyun Lee, Ha Young Kim, Sunmee Jang
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(3):562-570. Published online September 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.659
- 4,931 View
- 178 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Long-term glucocorticoid use increases fracture risk by reducing bone mass. This study evaluated the relationship between hip and vertebral fractures and the total amount of systematic glucocorticoid use.
Methods
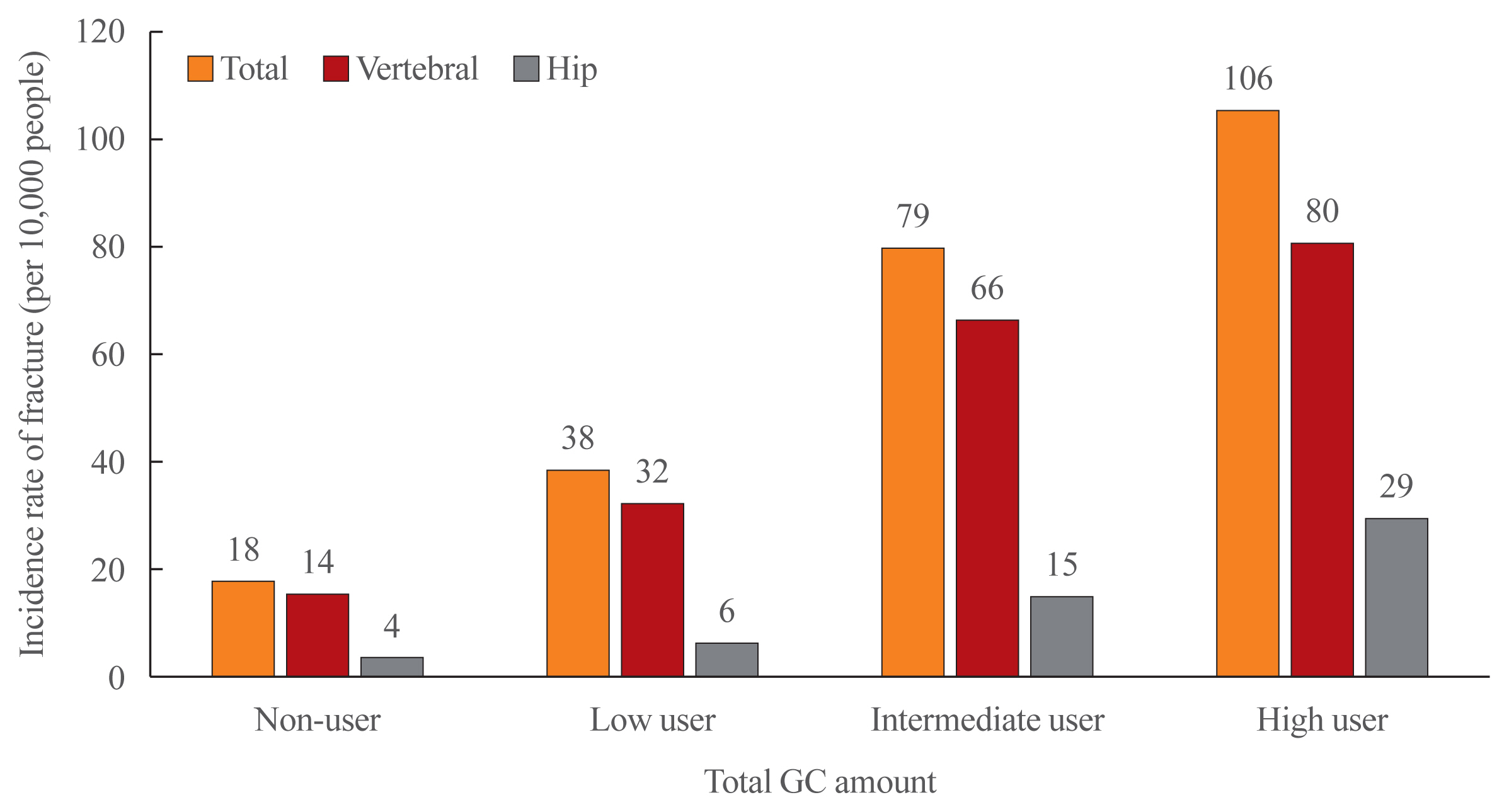
We randomly selected 1,896,159 people aged 20 to 100 years who participated in the National Health Checkup program in 2006. The amount of glucocorticoids prescribed was calculated based on the defined daily dose (DDD). The total DDD was obtained by adding oral and parenteral glucocorticoids for 6 months from the index date. Subjects were categorized into four groups according to total glucocorticoid DDDs: non-users (DDDs=0), low users (0< DDDs ≤45), intermediate users (45< DDDs ≤90), and high users (90< DDDs). We followed them for 2 years. A multivariate Cox proportional hazard model was used to evaluate the effects of the total amount of glucocorticoid use on hip and vertebral fractures.
Results
Higher glucocorticoid use was associated with a higher risk of vertebral fracture. Relative to non-users, the vertebral fracture risk was 1.39 times higher in the low-user group, 1.94 times higher in the intermediate-user group, and 2.43 times higher in the highuser group. The risk of hip fracture was 1.72 times higher in intermediate users and 3.28 times higher in high users than in non-users.
Conclusion
As the amount of glucocorticoid use for 6 months increased, the risk of hip and vertebral fractures became higher. In order to prevent fractures, it is necessary for doctors to evaluate the total amount of glucocorticoid prescribed to the patient and to provide appropriate treatment. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Average daily glucocorticoid dose, number of prescription days, and cumulative dose in the initial 90 days of glucocorticoid therapy are associated with subsequent hip and clinical vertebral fracture risk: a retrospective cohort study using a nationwide h
Masayuki Iki, Kenji Fujimori, Shinichi Nakatoh, Junko Tamaki, Shigeyuki Ishii, Nobukazu Okimoto, Hironori Imano, Sumito Ogawa
Osteoporosis International.2024; 35(5): 805. CrossRef - Chronic airway disease as a major risk factor for fractures in osteopenic women: Nationwide cohort study
Sung Hye Kong, Ae Jeong Jo, Chan Mi Park, Kyun Ik Park, Ji Eun Yun, Jung Hee Kim
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Bad to the bones: prescribing of drugs for the prevention and treatment of osteoporosis in patients on chronic glucocorticoids
Sarah J. Billups, Vinh K Thai, Jacob Denkins, Ian C. Dettman, Micol S. Rothman
Archives of Osteoporosis.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - High Risk of Fractures Within 7 Years of Diagnosis in Asian Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
Hyung Jin Ahn, Ye-Jee Kim, Ho-Su Lee, Jin Hwa Park, Sung Wook Hwang, Dong-Hoon Yang, Byong Duk Ye, Jeong-Sik Byeon, Seung-Jae Myung, Suk-Kyun Yang, Beom-Jun Kim, Sang Hyoung Park
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2022; 20(5): e1022. CrossRef - Challenges in the diagnosis and management of glucocorticoid‐induced osteoporosis in younger and older adults
Madhuni Herath, Bente Langdahl, Peter R. Ebeling, Frances Milat
Clinical Endocrinology.2022; 96(4): 460. CrossRef - Comparative effectiveness of bisphosphonate treatments for the prevention of re-fracture in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis: protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis
Hongmin Chu, Bo-Hyoung Jang, GaYoon Kim, Seowoo Bae, Hyeju Lee, Seonghee Nam, Jeonghoon Ahn
BMJ Open.2022; 12(9): e062537. CrossRef - Why Do We Need Proactive Management for Fracture Prevention in Long-Term Glucocorticoid Users?
Han Seok Choi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(3): 549. CrossRef
- Average daily glucocorticoid dose, number of prescription days, and cumulative dose in the initial 90 days of glucocorticoid therapy are associated with subsequent hip and clinical vertebral fracture risk: a retrospective cohort study using a nationwide h

- Hypothalamus and Pituitary gland
- Medical Treatment with Somatostatin Analogues in Acromegaly: Position Statement
- Sang Ouk Chin, Cheol Ryong Ku, Byung Joon Kim, Sung-Woon Kim, Kyeong Hye Park, Kee Ho Song, Seungjoon Oh, Hyun Koo Yoon, Eun Jig Lee, Jung Min Lee, Jung Soo Lim, Jung Hee Kim, Kwang Joon Kim, Heung Yong Jin, Dae Jung Kim, Kyung Ae Lee, Seong-Su Moon, Dong Jun Lim, Dong Yeob Shin, Se Hwa Kim, Min Jeong Kwon, Ha Young Kim, Jin Hwa Kim, Dong Sun Kim, Chong Hwa Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(1):53-62. Published online March 21, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.1.53
- 6,487 View
- 255 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub The Korean Endocrine Society (KES) published clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of acromegaly in 2011. Since then, the number of acromegaly cases, publications on studies addressing medical treatment of acromegaly, and demands for improvements in insurance coverage have been dramatically increasing. In 2017, the KES Committee of Health Insurance decided to publish a position statement regarding the use of somatostatin analogues in acromegaly. Accordingly, consensus opinions for the position statement were collected after intensive review of the relevant literature and discussions among experts affiliated with the KES, and the Korean Neuroendocrine Study Group. This position statement includes the characteristics, indications, dose, interval (including extended dose interval in case of lanreotide autogel), switching and preoperative use of somatostatin analogues in medical treatment of acromegaly. The recommended approach is based on the expert opinions in case of insufficient clinical evidence, and where discrepancies among the expert opinions were found, the experts voted to determine the recommended approach.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hydrogel-fiber-mesh-based 3D cell cultures: A new method for studying pituitary tumors
Wooju Jeong, Sungrok Wang, Yumin Kim, Soohyun Lee, Minhu Huang, Jaeil Park, Myung-Han Yoon, Chang-Myung Oh, Cheol Ryong Ku
Smart Materials in Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Bone Health in Patients with Thyroid Diseases: A Position Statement of the Korean Thyroid Association
A Ram Hong, Ho-Cheol Kang
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(2): 175. CrossRef - Growth Hormone Excess: Implications and Management
Suneela Dhaneshwar, Shrishti Shandily, Vatsalya Tiwari
Endocrine, Metabolic & Immune Disorders - Drug Targets.2023; 23(6): 748. CrossRef - Revisiting the usefulness of the short acute octreotide test to predict treatment outcomes in acromegaly
Montserrat Marques-Pamies, Joan Gil, Elena Valassi, Marta Hernández, Betina Biagetti, Olga Giménez-Palop, Silvia Martínez, Cristina Carrato, Laura Pons, Rocío Villar-Taibo, Marta Araujo-Castro, Concepción Blanco, Inmaculada Simón, Andreu Simó-Servat, Gemm
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Bone Health in Patients with Thyroid Diseases: a Position Statement from the Korean Thyroid Association
A Ram Hong, Hwa Young Ahn, Bu Kyung Kim, Seong Hee Ahn, So Young Park, Min-Hee Kim, Jeongmin Lee, Sun Wook Cho, Ho-Cheol Kang
International Journal of Thyroidology.2022; 15(1): 1. CrossRef - Octreotide in the treatment of acromegaly – the possibilities of high-dose therapy
I. A. Ilovayskaya
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2022; (10): 148. CrossRef - Approach of Acromegaly during Pregnancy
Alexandru Dan Popescu, Mara Carsote, Ana Valea, Andreea Gabriela Nicola, Ionela Teodora Dascălu, Tiberiu Tircă, Jaqueline Abdul-Razzak, Mihaela Jana Țuculină
Diagnostics.2022; 12(11): 2669. CrossRef - Left to themselves: Time to target chronic pain in childhood rare diseases
Christine B. Sieberg, Alyssa Lebel, Erin Silliman, Scott Holmes, David Borsook, Igor Elman
Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews.2021; 126: 276. CrossRef - Severe respiratory failure in a patient with COVID-19 and acromegaly: rapid improvement after adding octreotide
Jacob Luty, LesleAnn Hayward, Melanie Jackson, P Barton Duell
BMJ Case Reports.2021; 14(8): e243900. CrossRef - Precision Therapy in Acromegaly Caused by Pituitary Tumors: How Close Is It to Reality?
Cheol Ryong Ku, Vladimir Melnikov, Zhaoyun Zhang, Eun Jig Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(2): 206. CrossRef - Medical Treatment with Somatostatin Analogues in Acromegaly: Position Statement
Sang Ouk Chin, Cheol Ryong Ku, Byung Joon Kim, Sung-Woon Kim, Kyeong Hye Park, Kee Ho Song, Seungjoon Oh, Hyun Koo Yoon, Eun Jig Lee, Jung Min Lee, Jung Soo Lim, Jung Hee Kim, Kwang Joon Kim, Heung Yong Jin, Dae Jung Kim, Kyung Ae Lee, Seong-Su Moon, Dong
The Korean Journal of Medicine.2019; 94(6): 485. CrossRef
- Hydrogel-fiber-mesh-based 3D cell cultures: A new method for studying pituitary tumors

- Clinical Study
- Urinary Albumin Excretion Reflects Cardiovascular Risk in Postmenopausal Women without Diabetes: The 2011 to 2013 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Hee Jung Ahn, Do Sik Moon, Da Yeong Kang, Jung In Lee, Da Young Kim, Jin Hwa Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Hak Yeon Bae
- Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(4):537-546. Published online November 3, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.4.537
- 3,562 View
- 31 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The objective of the current study was to determine whether there was an association between urinary albumin excretion and cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk by estimating the Framingham Risk Score (FRS) in postmenopausal women without diabetes.
Methods This study was based on data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, which was conducted by the Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare in 2011 to 2013. Data on 2,316 postmenopausal women from a total of 24,594 participants was included in the analysis.
Results The mean FRS was significantly different in each of the urinary albumin to creatinine ratio (UACR) subgroups, and it increased with UACR. The FRS was 12.69±0.12 in the optimal group, 14.30±0.19 in the intermediate normal group, 14.62±0.26 in the high normal group, and 15.86±0.36 in the microalbuminuria group. After fully adjusting for potential confounding factors, high normal levels and microalbuminuria were significantly associated with the highest tertile of FRS ([odds ratio (OR), 1.642; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.124 to 2.400] and [OR, 3.385; 95% CI, 2.088 to 5.488], respectively) compared with the optimal subgroup. High normal levels and microalbuminuria were also significantly associated with a ≥10% 10-year risk of CVD ([OR, 1.853; 95% CI, 1.122 to 3.060] and [OR, 2.831; 95% CI, 1.327 to 6.037], respectively) after adjusting for potential confounding covariates.
Conclusion Urinary albumin excretion reflects CVD risk in postmenopausal women without diabetes, and high normal levels and microalbuminuria were independently associated with a higher risk of CVD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between urinary albumin creatinine ratio and cardiovascular disease
Yoo Jin Kim, Sang Won Hwang, Taesic Lee, Jun Young Lee, Young Uh, Gulali Aktas
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(3): e0283083. CrossRef - Relationship between Hypertension and the Declining Renal Function in Korean Adults
Jun Ho Lee
The Korean Journal of Clinical Laboratory Science.2021; 53(1): 32. CrossRef - Significance of Obstetrical History with Future Cardiovascular Disease Risk
Emmanuel Bassily, Cameron Bell, Sean Verma, Nidhi Patel, Aarti Patel
The American Journal of Medicine.2019; 132(5): 567. CrossRef - Articles inEndocrinology and Metabolismin 2016
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 62. CrossRef
- Association between urinary albumin creatinine ratio and cardiovascular disease

- Thyroid
- A Calcitonin-Negative Neuroendocrine Tumor Derived from Follicular Lesions of the Thyroid
- Ga Young Kim, Chul Yun Park, Chang Ho Cho, June Sik Park, Eui Dal Jung, Eon Ju Jeon
- Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(2):221-225. Published online December 9, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.2.221
- 3,396 View
- 30 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Neuroendocrine lesions of the thyroid are rare. The most common types are medullary thyroid carcinomas (MTCs) and C-cell hyperplasia. MTCs originate from thyroid parafollicular cells that secrete calcitonin which serves as a serum marker of MTCs. Here, the rare case of a calcitonin-negative neuroendocrine tumor (NET) derived from follicular lesions of the thyroid is described. A 34-year-old man presented at our hospital for the surgical management of an incidental thyroid nodule that was observed on an ultrasound sonography (USG) of the neck. Initially, USG-guided aspiration cytology was performed, and a MTC was suspected. The expressions of thyroglobulin and thyroid transcription factor-1, which are thyroid follicular cell markers, and synaptophysin and chromogranin A, which are neuroendocrine markers, was confirmed following surgical pathology. However, the staining of calcitonin, a marker of MTCs, was not observed. A nonmedullary NET of the thyroid is uncommon, and the distinction between calcitonin-negative NETs and MTCs of the thyroid may be important due to differences in their clinical courses and management.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Calcitonin-Negative Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Thyroid Gland: Case Report and Literature Review
Ricardo Fernández-Ferreira, Ildefonso Roberto De la Peña-López, Karla Walkiria Zamudio-Coronado, Luis Antonio Delgado-Soler, María Eugenia Torres-Pérez, Christianne Bourlón-de los Ríos, Rubén Cortés-González
Case Reports in Oncology.2021; 14(1): 112. CrossRef - Calcitonin-negative neuroendocrine tumor of the thyroid with metastasis to liver-rare presentation of an unusual tumor: A case report and review of literature
Huai-Jie Cai, Han Wang, Nan Cao, Bin Huang, Fan-Lei Kong, Li-Ren Lu, Ya-Yuan Huang, Wei Wang
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2020; 8(1): 179. CrossRef - Medullary thyroid carcinoma with double negative calcitonin and CEA: a case report and update of literature review
Claudio Gambardella, Chiara Offi, Guglielmo Clarizia, Roberto Maria Romano, Immacolata Cozzolino, Marco Montella, Rosa Maria Di Crescenzo, Massimo Mascolo, Angelo Cangiano, Sergio Di Martino, Giancarlo Candela, Giovanni Docimo
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Calcitonin negative Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: a challenging diagnosis or a medical dilemma?
Claudio Gambardella, Chiara Offi, Renato Patrone, Guglielmo Clarizia, Claudio Mauriello, Ernesto Tartaglia, Francesco Di Capua, Sergio Di Martino, Roberto Maria Romano, Lorenzo Fiore, Alessandra Conzo, Giovanni Conzo, Giovanni Docimo
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Calcitonin-Negative Neuroendocrine Tumor of the Thyroid
Megan Parmer, Stacey Milan, Alireza Torabi
International Journal of Surgical Pathology.2017; 25(2): 191. CrossRef - Clinical and pathological analysis of 19 cases of medullary thyroid carcinoma without an increase in calcitonin
Qiufeng Zhou, Shuanglei Yue, Ye Cheng, Ju Jin, Haimiao Xu
Experimental and Toxicologic Pathology.2017; 69(8): 575. CrossRef - Primary Calcitonin-negative Neuroendocrine Tumor
Sabri Özden, Aysel Colak, Baris Saylam, Ömer Cengiz
World Journal of Endocrine Surgery.2017; 9(3): 104. CrossRef - LONG-TERM RESULTS OF SURGICAL TREATMENT OF PATIENTS WITH FOLLICULAR TUMORS OF THE THYROID
I. N. Zubarovskiy, M. V. Mikhailova, S. K. Osipenko
Grekov's Bulletin of Surgery.2015; 174(5): 32. CrossRef
- Calcitonin-Negative Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Thyroid Gland: Case Report and Literature Review

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Regulation of Adipocyte Differentiation via MicroRNAs
- You Hwa Son, Sojeong Ka, A Young Kim, Jae Bum Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(2):122-135. Published online June 26, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.2.122
- 6,796 View
- 104 Download
- 75 Web of Science
- 72 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Adipocyte differentiation, termed adipogenesis, is a complicated process in which pluripotent mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into mature adipocytes. The process of adipocyte differentiation is tightly regulated by a number of transcription factors, hormones and signaling pathway molecules. Recent studies have demonstrated that microRNAs, which belong to small noncoding RNA species, are also involved in adipocyte differentiation.
In vivo andin vitro studies have revealed that various microRNAs affect adipogenesis by targeting several adipogenic transcription factors and key signaling molecules. In this review, we will summarize the roles of microRNAs in adipogenesis and their target genes associated with each stage of adipocyte differentiation.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A review of the role of transcription factors in regulating adipogenesis and lipogenesis in beef cattle
Belete Kuraz Abebe, Hongbao Wang, Anning Li, Linsen Zan
Journal of Animal Breeding and Genetics.2024; 141(3): 235. CrossRef - A review of the role of epigenetic studies for intramuscular fat deposition in beef cattle
Belete Kuraz Abebe, Jianfang Wang, Juntao Guo, Hongbao Wang, Anning Li, Linsen Zan
Gene.2024; 908: 148295. CrossRef - Transcriptome analysis of miRNAs during myoblasts adipogenic differentiation
Chengchuang Song, Xue Fang, Qi Wang, Yaqi Chen, Bei Zhao, Yanhong Wang, Xingtang Fang, Chunlei Zhang
Animal Biotechnology.2023; 34(4): 1406. CrossRef - Advances in the regulation of adipogenesis and lipid metabolism by exosomal ncRNAs and their role in related metabolic diseases
Cong Liu, Xilin Liu, Hong Li, Zhichen Kang
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Indian gooseberry and barley sprout mixture prevents obesity by regulating adipogenesis, lipogenesis, and lipolysis in C57BL/6J mice with high-fat diet-induced obesity
Soo-Jeung Park, Jong-Lae Kim, Mi-Ryeong Park, Jong Wook Lee, Ok-Kyung Kim, Jeongmin Lee
Journal of Functional Foods.2022; 90: 104951. CrossRef - Interleukin-6 mimics insulin-dependent cellular distribution of some cytoskeletal proteins and Glut4 transporter without effect on glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
Maciej Błaszczyk, Małgorzata Gajewska, Marta Dymowska, Alicja Majewska, Tomasz Domoradzki, Adam Prostek, Rafał Pingwara, Magdalena Hulanicka, Katarzyna Grzelkowska-Kowalczyk
Histochemistry and Cell Biology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Heat-Killed Enterococcus faecalis Prevents Adipogenesis and High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity by Inhibition of Lipid Accumulation through Inhibiting C/EBP-α and PPAR-γ in the Insulin Signaling Pathway
Jin-Ho Lee, Keun-Jung Woo, Min-Ah Kim, Joonpyo Hong, Jihee Kim, Sun-Hong Kim, Kwon-Il Han, Masahiro Iwasa, Tack-Joong Kim
Nutrients.2022; 14(6): 1308. CrossRef - The delivery of miR-21a-5p by extracellular vesicles induces microglial polarization via the STAT3 pathway following hypoxia-ischemia in neonatal mice
Dan-Qing Xin, Yi-Jing Zhao, Ting-Ting Li, Hong-Fei Ke, Cheng-Cheng Gai, Xiao-Fan Guo, Wen-Qiang Chen, De-Xiang Liu, Zhen Wang
Neural Regeneration Research.2022; 17(10): 2238. CrossRef - Extracellular Vesicles from Adipose Tissue Could Promote Metabolic Adaptation through PI3K/Akt/mTOR
Jaime Delgadillo-Velázquez, Herminia Mendivil-Alvarado, Carlos Daniel Coronado-Alvarado, Humberto Astiazaran-Garcia
Cells.2022; 11(11): 1831. CrossRef - Adipocyte differentiation between obese and lean conditions depends on changes in miRNA expression
Yerim Heo, Hyunjung Kim, Jiwon Lim, Sun Shim Choi
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Selected Non-Coding RNAs and Gene Expression Profiles between Common Osteosarcoma Cell Lines
Mateusz Sikora, Katarzyna Krajewska, Klaudia Marcinkowska, Anna Raciborska, Rafał Jakub Wiglusz, Agnieszka Śmieszek
Cancers.2022; 14(18): 4533. CrossRef - Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secreted-Extracellular Vesicles are Involved in Chondrocyte Production and Reduce Adipogenesis during Stem Cell Differentiation
Yu-Chen Tsai, Tai-Shan Cheng, Hsiu-Jung Liao, Ming-Hsi Chuang, Hui-Ting Chen, Chun-Hung Chen, Kai-Ling Zhang, Chih-Hung Chang, Po-Cheng Lin, Chi-Ying F. Huang
Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine.2022; 19(6): 1295. CrossRef - Tissue and circulating microRNAs as biomarkers of response to obesity treatment strategies
G. Catanzaro, T. Filardi, C. Sabato, A. Vacca, S. Migliaccio, S. Morano, E. Ferretti
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2021; 44(6): 1159. CrossRef - Benzyl Butyl Phthalate Induced Early lncRNA H19 Regulation in C3H10T1/2 Stem Cell Line
Jian Zhang, Mahua Choudhury
Chemical Research in Toxicology.2021; 34(1): 54. CrossRef - Inhibition of preadipocyte differentiation by Lycium barbarum polysaccharide treatment in 3T3-L1 cultures
Xiaochun Xu, Wenjuan Chen, Shukun Yu, Qian Lei, Lihong Han, Wenping Ma
Electronic Journal of Biotechnology.2021; 50: 53. CrossRef - MiR-25-3p regulates the differentiation of intramuscular preadipocytes in goat via targeting <i>KLF4</i>
Yu Du, Yue Zhao, Yong Wang, Qingyong Meng, Jiangjiang Zhu, Yaqiu Lin
Archives Animal Breeding.2021; 64(1): 17. CrossRef - MiR-208b Regulates Rabbit Preadipocyte Proliferation and Differentiation
Jiahao Shao, Ting Pan, Jie Wang, Tao Tang, Yanhong Li, Xianbo Jia, Songjia Lai
Genes.2021; 12(6): 890. CrossRef - Comparing the effect of cinnamaldehyde and metformin on expression of MiR320 and MiR26-b in insulin resistant 3T3L1 adipocytes
Yousof Naghiaee, Mahmood Vakili, Mohammad Mohammadi, Azra Mohiti, Javad Mohiti-Ardakani
Phytomedicine Plus.2021; 1(4): 100122. CrossRef - Lower miR‐26a levels in breastmilk affect gene expression in adipose tissue of offspring
Catalina A. Pomar, Francisca Serra, Andreu Palou, Juana Sánchez
The FASEB Journal.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - MicroRNA-378 regulates adipogenic differentiation in bovine intramuscular preadipocytes by targeting CaMKK2
Dongwei Li, Heng Wang, Yongmin Li, Changqing Qu, Yunhai Zhang, Hongyu Liu, Xiaorong Zhang
Adipocyte.2021; 10(1): 483. CrossRef - miR-6315 Attenuates Methotrexate Treatment-Induced Decreased Osteogenesis and Increased Adipogenesis Potentially through Modulating TGF-β/Smad2 Signalling
Ya-Li Zhang, Liang Liu, Yu-Wen Su, Cory J. Xian
Biomedicines.2021; 9(12): 1926. CrossRef - Inhibitory Effects of Pinostilbene on Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes: A Study of Possible Mechanisms
You Chul Chung, Chang-Gu Hyun
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(24): 13446. CrossRef - Regulation of Methylase METTL3 on Fat Deposition
Gang Luo, Jialing Chen, Zhanjun Ren
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 4843. CrossRef - miR-214-5p Regulating Differentiation of Intramuscular Preadipocytes in Goats via Targeting KLF12
Yu Du, Yong Wang, Yanyan Li, Quzhe Emu, Jiangjiang Zhu, Yaqiu Lin
Frontiers in Genetics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Screening and identification of MicroRNAs expressed in perirenal adipose tissue during rabbit growth
Guoze Wang, Guo Guo, Xueting Tian, Shenqiang Hu, Kun Du, Qinghai Zhang, Jingxin Mao, Xianbo Jia, Shiyi Chen, Jie Wang, Songjia Lai
Lipids in Health and Disease.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Descending Expression of miR320 in Insulin-Resistant Adipocytes Treated with Ascending Concentrations of Metformin
Yousof Naghiaee, Reza Didehdar, Zahra Malekpour-Dehkordi, Fatemeh Pourrajab, Javad Mohiti-Ardakani
Biochemical Genetics.2020; 58(5): 661. CrossRef - Citrus aurantium L. Dry Extracts Ameliorate Adipocyte Differentiation of 3T3-L1 Cells Exposed to TNFα by Down-Regulating miR-155 Expression
Michele Campitelli, Antonella Desiderio, Giuseppe Cacace, Cecilia Nigro, Immacolata Prevenzano, Alessia Leone, Sonia de Simone, Pietro Campiglia, Pietro Formisano, Gregory A. Raciti, Francesco Beguinot, Claudia Miele
Nutrients.2020; 12(6): 1587. CrossRef - Metabolic Benefits of MicroRNA-22 Inhibition
Marc Thibonnier, Christine Esau
Nucleic Acid Therapeutics.2020; 30(2): 104. CrossRef - Differentially Expressed miRNA-Gene Targets Related to Intramuscular Fat in Musculus Longissimus Dorsi of Charolais × Holstein F2-Crossbred Bulls
Bilal Ahmad Mir, Henry Reyer, Katrin Komolka, Siriluck Ponsuksili, Christa Kühn, Steffen Maak
Genes.2020; 11(6): 700. CrossRef - MiR224-5p Inhibitor Restrains Neuronal Apoptosis by Targeting NR4A1 in the Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation (OGD) Model
Ling-Ling Liu, Shan Qiao, Mei-Ling Wang, Huai-Kuan Wu, Yong-Xin Su, Ke-Mo Wang, Xue-Wu Liu
Frontiers in Neuroscience.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Adipogenesis: A Complex Interplay of Multiple Molecular Determinants and Pathways
Melvin A. Ambele, Priyanka Dhanraj, Rachel Giles, Michael S. Pepper
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(12): 4283. CrossRef - MicroRNA‑449a regulates the progression of brain aging by targeting SCN2B in SAMP8 mice
Ya‑Xin Tan, Ying Hong, Shui Jiang, Min‑Nan Lu, Shan Li, Bo Chen, Li Zhang, Tao Hu, Rui Mao, Rong Mei, Yan‑Bin Xiyang
International Journal of Molecular Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of adenovirus 36 seropositivity on the expression of adipogenic microRNAs in obese subjects
Víctor Manríquez, Alvaro Gutierrez, Alexis Morales, Roberto Brito, Monica Pavez, Jorge Sapunar, Luis Fonseca, Víctor Molina, Eugenia Ortiz, Maria Ines Barra, Camila Reimer, Maria Charles, Constance Schneider, Alvaro Cerda
International Journal of Obesity.2020; 44(11): 2303. CrossRef - Metformin downregulates miR223 expression in insulin-resistant 3T3L1 cells and human diabetic adipose tissue
Yousof Naghiaee, Reza Didehdar, Fatemeh Pourrajab, Masoud Rahmanian, Naeime Heiranizadeh, Azra Mohiti, Javad Mohiti-Ardakani
Endocrine.2020; 70(3): 498. CrossRef - Metabolic and energetic benefits of microRNA-22 inhibition
Marc Thibonnier, Christine Esau, Sujoy Ghosh, Edward Wargent, Claire Stocker
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2020; 8(1): e001478. CrossRef - Bta-miR-376a Targeting KLF15 Interferes with Adipogenesis Signaling Pathway to Promote Differentiation of Qinchuan Beef Cattle Preadipocytes
Xingyi Chen, Sayed Haidar Abbas Raza, Gong Cheng, Xinhao Ma, Jianfang Wang, Linsen Zan
Animals.2020; 10(12): 2362. CrossRef - The cross-talk between adipokines and miRNAs in health and obesity-mediated diseases
Ahmad Ghasemi, Seyed Isaac Hashemy, Mohsen Azimi-Nezhad, Alireza Dehghani, Jafar Saeidi, Mahnaz Mohtashami
Clinica Chimica Acta.2019; 499: 41. CrossRef - MicroRNAs and long noncoding RNAs: new regulators in cell fate determination of mesenchymal stem cells
Zixiang Wu, Shujing Liang, Wenyu Kuai, Lifang Hu, Airong Qian
RSC Advances.2019; 9(64): 37300. CrossRef - Harnessing adipogenesis to prevent obesity
Nida Haider, Louise Larose
Adipocyte.2019; 8(1): 98. CrossRef - MiR‐127 attenuates adipogenesis by targeting MAPK4 and HOXC6 in porcine adipocytes
Yun Gao, Yingqian Wang, Xiaochang Chen, Ying Peng, Fenfen Chen, Yulin He, Weijun Pang, Gongshe Yang, Taiyong Yu
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2019; 234(12): 21838. CrossRef - MicroRNA-425 controls lipogenesis and lipolysis in adipocytes
Renli Qi, Jing Wang, Qi Wang, Xiaoyu Qiu, Feiyun Yang, Zuohua Liu, Jinxiu Huang
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids.2019; 1864(5): 744. CrossRef - miRNA-7a-2-3p Inhibits Neuronal Apoptosis in Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation (OGD) Model
Zi-Bin Zhang, Ya-Xin Tan, Qiong Zhao, Liu-Lin Xiong, Jia Liu, Fei-Fei Xu, Yang Xu, Larisa Bobrovskaya, Xin-Fu Zhou, Ting-Hua Wang
Frontiers in Neuroscience.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - IL‐1α inhibits proliferation and adipogenic differentiation of human adipose‐derived mesenchymal stem cells through NF‐κB‐ and ERK1/2‐mediated proinflammatory cytokines
Xuerong Sun, Tangbin Zou, Changqing Zuo, Mingmeng Zhang, Benyan Shi, Zhiwen Jiang, Hongjing Cui, Xiaoxin Liao, Xiaoyi Li, Yuelian Tang, Yusheng Liu, Xinguang Liu
Cell Biology International.2018; 42(7): 794. CrossRef - MicroRNA‐224‐5p regulates adipocyte apoptosis induced by TNFα via controlling NF‐κB activation
Renli Qi, Jinxiu Huang, Qi Wang, Hong Liu, Ruisheng Wang, Jing Wang, Feiyun Yang
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2018; 233(2): 1236. CrossRef - Potential role of microRNAs in the regulation of adipocytes liposecretion and adipose tissue physiology
Giulia Maurizi, Lucia Babini, Lucio Della Guardia
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2018; 233(12): 9077. CrossRef - Chronic hyperinsulinemia induced miR-27b is linked to adipocyte insulin resistance by targeting insulin receptor
Ankita Srivastava, Kripa Shankar, Muheeb Beg, Sujith Rajan, Abhishek Gupta, Salil Varshney, Durgesh Kumar, Sanchita Gupta, Raj Kumar Mishra, Anil Nilkanth Gaikwad
Journal of Molecular Medicine.2018; 96(3-4): 315. CrossRef - Bta-miR-130a/b regulates preadipocyte differentiation by targeting PPARG and CYP2U1 in beef cattle
Xueyao Ma, Dawei Wei, Gong Cheng, Shijun Li, Li Wang, Yaning Wang, Xiaoyu Wang, Song Zhang, Hongbao Wang, Linsen Zan
Molecular and Cellular Probes.2018; 42: 10. CrossRef - Transdifferentiation of adipocytes to osteoblasts: potential for orthopaedic treatment
Daphne P L Lin, Crispin R Dass
Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology.2018; 70(3): 307. CrossRef - Characterization of miRNA transcriptome profiles related to breast muscle development and intramuscular fat deposition in chickens
Shouyi Fu, Yinli Zhao, Yuanfang Li, Guoxi Li, Yi Chen, Zhuanjian Li, Guirong Sun, Hong Li, Xiangtao Kang, Fengbin Yan
Journal of Cellular Biochemistry.2018; 119(8): 7063. CrossRef - Transcriptomic Analyses of Adipocyte Differentiation From Human Mesenchymal Stromal‐Cells (MSC)
Antonio Casado‐Díaz, Jaouad Anter, Sören Müller, Peter Winter, José Manuel Quesada‐Gómez, Gabriel Dorado
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2017; 232(4): 771. CrossRef - Downregulated miR-29a/b/c during Contact Inhibition Stage Promote 3T3-L1 Adipogenesis by Targeting DNMT3A
Yingjie Zhu, Guangyong Zheng, Huichao Wang, Yudong Jia, Ying Zhang, Yanfeng Tang, Wenlong Li, Yanan Fan, Xiaodong Zhang, Youwen Liu, Sanhong Liu, Makoto Kanzaki
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(1): e0170636. CrossRef - Potential miRNA involvement in the anti-adipogenic effect of resveratrol and its metabolites
Itziar Eseberri, Arrate Lasa, Jonatan Miranda, Ana Gracia, Maria P. Portillo, Cristina Óvilo
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(9): e0184875. CrossRef - Identification and characterization of differentially expressed miRNAs in subcutaneous adipose between Wagyu and Holstein cattle
Yuntao Guo, Xiuxiu Zhang, Wanlong Huang, Xiangyang Miao
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Integrated analysis of mRNA and miRNA expression profiles in livers of Yimeng black pigs with extreme phenotypes for backfat thickness
Wentong Li, Yalan Yang, Ying Liu, Shuai Liu, Xiuxiu Li, Yingping Wang, Yanmin Zhang, Hui Tang, Rong Zhou, Kui Li
Oncotarget.2017; 8(70): 114787. CrossRef - Small non coding RNAs in adipocyte biology and obesity
Ez-Zoubir Amri, Marcel Scheideler
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2017; 456: 87. CrossRef - Role of MicroRNA Regulation in Obesity-Associated Breast Cancer: Nutritional Perspectives
Ravi Kasiappan, Dheeran Rajarajan
Advances in Nutrition.2017; 8(6): 868. CrossRef - Biomolecular features of inflammation in obese rheumatoid arthritis patients: management considerations
Barbara Tolusso, Stefano Alivernini, Maria Rita Gigante, Gianfranco Ferraccioli, Elisa Gremese
Expert Review of Clinical Immunology.2016; 12(7): 751. CrossRef - Circulating microRNAs are deregulated in overweight/obese children: preliminary results of the I.Family study
Giuseppe Iacomino, Paola Russo, Ilaria Stillitano, Fabio Lauria, Pasquale Marena, Wolfgang Ahrens, Pasquale De Luca, Alfonso Siani
Genes & Nutrition.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of MicroRNAs in NAFLD/NASH
Gyongyi Szabo, Timea Csak
Digestive Diseases and Sciences.2016; 61(5): 1314. CrossRef - MicroRNA‐29b promotes the adipogenic differentiation of human adipose tissue‐derived stromal cells
Xi‐Mei Zhang, Li‐Hong Wang, Dong‐Ju Su, Dan Zhu, Qiu‐Ming Li, Mei‐Hua Chi
Obesity.2016; 24(5): 1097. CrossRef - MiR-181a-5p regulates 3T3-L1 cell adipogenesis by targeting <italic>Smad7</italic> and <italic>Tcf7l2</italic>
Dan Ouyang, Lifeng Xu, Lihua Zhang, Dongguang Guo, Xiaotong Tan, Xiaofang Yu, Junjie Qi, Yaqiong Ye, Qihong Liu, Yongjiang Ma, Yugu Li
Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica.2016; 48(11): 1034. CrossRef - Metformin-suppressed differentiation of human visceral preadipocytes: Involvement of microRNAs
Koji Fujita, Hisakazu Iwama, Kyoko Oura, Tomoko Tadokoro, Kayo Hirose, Miwako Watanabe, Teppei Sakamoto, Akiko Katsura, Shima Mimura, Takako Nomura, Joji Tani, Hisaaki Miyoshi, Asahiro Morishita, Hirohito Yoneyama, Keiichi Okano, Yasuyuki Suzuki, Takashi
International Journal of Molecular Medicine.2016; 38(4): 1135. CrossRef - Systematic study of cis-antisense miRNAs in animal species reveals miR-3661 to target PPP2CA in human cells
Jian Wang, Zongcheng Li, Bailong Liu, Guangnan Chen, Ningsheng Shao, Xiaomin Ying, Ya Wang
RNA.2016; 22(1): 87. CrossRef - Oxidative stress, redox regulation and diseases of cellular differentiation
Zhi-Wei Ye, Jie Zhang, Danyelle M. Townsend, Kenneth D. Tew
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - General Subjects.2015; 1850(8): 1607. CrossRef - Noncoding RNAs, cytokines, and inflammation-related diseases
José Luiz Marques-Rocha, Mirian Samblas, Fermin I. Milagro, Josefina Bressan, J. Alfredo Martínez, Amelia Marti
The FASEB Journal.2015; 29(9): 3595. CrossRef - Polymorphism in miR-31 and miR-584 binding site in the angiotensinogen gene differentially influences body fat distribution in both sexes
Jan Machal, Jan Novak, Renata Hezova, Filip Zlamal, Anna Vasku, Ondrej Slaby, Julie Bienertova-Vasku
Genes & Nutrition.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Mitochondria-related miR-141-3p contributes to mitochondrial dysfunction in HFD-induced obesity by inhibiting PTEN
Juan Ji, Yufeng Qin, Jing Ren, Chuncheng Lu, Rong Wang, Xiuliang Dai, Ran Zhou, Zhenyao Huang, Miaofei Xu, Minjian Chen, Wei Wu, Ling Song, Hongbing Shen, Zhibin Hu, Dengshun Miao, Yankai Xia, Xinru Wang
Scientific Reports.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - MicroRNAs in Bone Balance and Osteoporosis
Junying Chen, Min Qiu, Ce Dou, Zhen Cao, Shiwu Dong
Drug Development Research.2015; 76(5): 235. CrossRef - Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2014
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 47. CrossRef - MicroRNA regulatory networks in human adipose tissue and obesity
Peter Arner, Agné Kulyté
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2015; 11(5): 276. CrossRef - Epigenomics, gestational programming and risk of metabolic syndrome
M Desai, J K Jellyman, M G Ross
International Journal of Obesity.2015; 39(4): 633. CrossRef - Expression Profiling and Structural Characterization of MicroRNAs in Adipose Tissues of Hibernating Ground Squirrels
Cheng-Wei Wu, Kyle K. Biggar, Kenneth B. Storey
Genomics, Proteomics & Bioinformatics.2014; 12(6): 284. CrossRef
- A review of the role of transcription factors in regulating adipogenesis and lipogenesis in beef cattle

- A Case of Adipsic Hypernatremia Associated with Anomalous Corpus Callosum in Adult with Mental Retardation.
- Boo Gyoung Kim, Ka Young Kim, Youn Jeong Park, Keun Suk Yang, Ji Hee Kim, Hee Chan Jung, Hee Chul Nam, Young Ok Kim, Yu Seon Yun
- Endocrinol Metab. 2012;27(3):232-236. Published online September 19, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2012.27.3.232
- 2,170 View
- 28 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Adipsic hypernatremia cause chronic hyperosmolality and hypernatremia through a combination of impaired thirst and osmotically stimulated antidiuretic hormone secretion. This syndrome can be grouped together as disorders of osmoreceptor dysfunction due to the various degrees of osmoreceptor destruction related with different types of intracranial lesions around the anterior hypothalamus, consistent with the location of primary osmoreceptor cells. Adipsic hypernatremia, associated with developmental disorder of corpus callosum, is very rare. Most cases are diagnosed at infancy and early childhood; the replacement of desmopressin is necessary. Herein, we report adipsic hypernatremia associated with anomalous corpus callosum in adult with mental retardation; they were treated with only free water without desmopressin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adipsic Hypernatremia after Clipping of a Ruptured Aneurysm in the Anterior Communicating Artery: A Case Report
Won Ki Kim, Taeho Lee, Ae Jin Kim, Han Ro, Jae Hyun Chang, Hyun Hee Lee, Wookyung Chung, Ji Yong Jung
Electrolytes & Blood Pressure.2021; 19(2): 56. CrossRef - The use of diffusion tractography to characterize a corpus callosum malformation in a dog
Philippa J. Johnson, Erica F. Barry, Wen‐Ming Luh, Emma Davies
Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine.2019; 33(2): 743. CrossRef
- Adipsic Hypernatremia after Clipping of a Ruptured Aneurysm in the Anterior Communicating Artery: A Case Report

- Visual Seizure: A Reversible Complication of Non-Ketotic Hyperglycemia.
- Na Young Kim, Min Su Park
- Endocrinol Metab. 2012;27(2):155-158. Published online June 20, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2012.27.2.155
- 18,789 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 65-year-old man with diabetes mellitus was presented with left visual aura, followed by a versive seizure, each lasting approximately 3 minutes. Neurological examination showed an intermittent left homonymous hemianopsia. Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed right occipital lobe lesion, with cytotoxic edema. Blood glucose was 593 mg/dL and serum osmolarity was 309 mOsm/kg. The seizures were controlled by normalization of blood sugar and short-term anticonvulsant, and the lesions were resolved in a follow-up MRI. We report a case of visual seizures associated with non-ketotic hyperglycemia.

- A Case of Adult-Onset Adrenoleukodystrophy Combined with Moyamoya Disease.
- Yong Cheol Kim, Byoung Hyun Park, Tae Yang Yu, Ae Ryoung Jin, Hye Jung Noh, Chung Yong Yang, Ha Young Kim, Chung Gu Cho
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2009;24(1):58-62. Published online March 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2009.24.1.58
- 2,452 View
- 54 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD) is a rare inherited metabolic disease associated with the accumulation of very long chain fatty acids (VLCFA) in the central and peripheral nervous systems and adrenal glands, and leads to leukoencephaly myeloneuropathy, adrenal insufficiency, and hypogonadism. Frequent phenotypes, which account for 80% of cases, are infantile ALD and adrenomyeloneuropathy. Adult-onset ALD is rare (1~3%). The diagnosis of X-linked ALD is based on clinical findings and abnormal plasma concentrations of VLCFA. Here, we report a rare case of adult-onset ALD, which might involve a brain vascular operation as an aggravating factor, combined with moyamoya disease, in a 35-year-old male who presented with adrenal insufficiency, abnormal brain imaging, and elevated VLCFA levels.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical and Genetic Aspects in Twelve Korean Patients with Adrenomyeloneuropathy
Hyung Jun Park, Ha Young Shin, Hoon-Chul Kang, Byung-Ok Choi, Bum Chun Suh, Ho Jin Kim, Young-Chul Choi, Phil Hyu Lee, Seung Min Kim
Yonsei Medical Journal.2014; 55(3): 676. CrossRef - An Incidentally Identified Sporadic Case with Adrenoleukodystrophy with the ABCD1 Mutation
Soon-Jung Shin, Ja Hye Kim, Yoo-Mi Kim, Gu-Hwan Kim, Beom Hee Lee, Han-Wook Yoo
Journal of Genetic Medicine.2013; 10(1): 43. CrossRef
- Clinical and Genetic Aspects in Twelve Korean Patients with Adrenomyeloneuropathy

- A Case of Pheochromocytoma That Presented as Inverted Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy.
- Meyoung Cho, Ik Sang Shin, Ae Ryoung Jin, Jong Bin Park, Hye Jung Noh, Hun Soo Kim, Ha Young Kim, Byoung Hyun Park, Chung Gu Cho, Jin Won Jeong
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2009;24(1):47-53. Published online March 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2009.24.1.47
- 1,800 View
- 20 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - A 52-year-old female was admitted to the hospital with abdominal pain. Her electrocardiogram revealed ST depressions in leads II, III, aVF and V2-5. The echocardiography showed transient cardiomyopathy with akinesia of the basal and mid portions of the left ventricle and hyperkinesia of the apex. There was no evidence of any vascular lesion on the emergency coronary angiography. She was diagnosed with pheochromocytoma by abdominal computed tomography and the post-operative pathologic examinations. These findings led us to a diagnosis of inverted Takotsubo cardiomyopathy related with pheochromocytoma. The recognition of such a rare cardiac manifestation should be considered in the diagnosis of pheochromocytoma, and especially in the circumstances of acute heart failure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Case of Malignant Pheochromocytoma Presenting as Inverted Takotsubo-Like Cardiomyopathy
Jung Eun Jang, Hyuk Hee Kwon, Min Jung Lee, Chang Hee Jung, Sung Jin Bae, Hong Kyu Kim, Woo Je Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2012; 27(1): 98. CrossRef
- A Case of Malignant Pheochromocytoma Presenting as Inverted Takotsubo-Like Cardiomyopathy

- Serum Leptin Levels in Relation to Quantitative Ultrasound Values of Calcaneus in Korean Postmenopausal Women in Chung-Up District.
- Sang Wook Kim, Jung Min Koh, Ha Young Kim, Duk Jae Kim, Ghi Su Kim
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2002;17(1):79-86. Published online February 1, 2002
- 1,004 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Obese postmenopausal women usually have a tend to have greater bone mineral density than lean women. This has been attributed to either the mechanical effects of their excessive weight on bone tissue or to their high body fat content. A recent study demonstrated that leptin, the hormone produced in adipocytes, acts on bone metabolism. These findings have prompted speculations on the possible role of leptin in the protective effect of obesity on bone. METHEODS: We studied the relationship between serum leptin levels and quantitative ultrasound (QUS) values of calcaneus in 94 postmenopausal Korean women who were randomly selected from the population of the Chung-Up osteoporosis prevalence study. QUS values, broadband ultrasound attenuation and speed of sound; were measured at the calcaneus. RESULTS: Leptin values were strongly correlated with body mass index (r = 0.478, p< 0.001), confirming a positive relationship between leptin levels and fat mass. In contrast, no significant correlations were observed between serum leptin levels and calcaneal QUS values. CONCLUSION: Our results suggest that circulating plasma leptin does not have a significant influence on QUS values of calcaneus in Korean postmenopausal women.

- Percutaneous Ethanol Injection in Autonomous Functioning Thyroid Nodules and Complex Cysts: Five Years' Experience.
- Seong Jin Lee, Jung Hee Han, Ha Young Kim, Jong Chul Won, Sang Wook Kim, Ho Kyu Lee, Il Min Ahn
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2002;17(1):57-68. Published online February 1, 2002
- 1,037 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Percutaneous ethanol injection therapy (PEI) performed with ultrasonography guidance has recently been used in cases of autonomous functioning thyroid nodules (AFTN) and benign complex cysts. We performed this study to analyze the effects of PEI on AFTN and benign complex cysts. METHEODS: From September 1995 to September 2000, we performed PEI on 456 outpatients (47 men and 409 women, mean age 42.4+/-11.8 years) with AFTN or benign complex cysts. All cases were subjected to fine needle aspirations (FNA) by ultrasonography-guidance if necessary. FNA was performed at least twice with results of colloid nodule in cases of complex cysts. For AFTN, cases with FNA results of follicular neoplasm were also included. After PEI on AFTN, patients were classified into three response groups: complete response as judged by our new criteria (CR, normalization of TSH and free T4, disappearance of hot nodule on thyroid scan) along with the old criteria of previous studies (normalization of TSH and free T4, recovery of suppressed extranodular tissue on thyroid scan), partial response (PR, normalized free T4 but suppressed TSH, persistent hot nodule despite recovery in suppressed extranodular tissue) and no response (no change of hot nodule). Complex cysts were classified into three groups in accordance with volume reduction after PEI: complete response (CR, above 90% of volume reduction), partial response (PR, 50~89%) and no response (below 50%). RESULTS: Overall pre-treatment volumes were 15.3+/-12.1 mL and post-treatment volumes were 2.8+/-2.9 mL, with 66.4+/-19.9% of volume reductions in AFTN and complex cysts. Volume reductions were 71.5+/-18.0% in AFTN, and 66.1+/-15.0% in complex cysts. In 24 cases of AFTN, responses satisfying the previous criteria were 14 (58.3%) of CR, 6 (25.0%) of PR, and 4 (16.7%) of no response. However, by the new criteria there were 1 (4.2%) of CR, 10 (41.6%) of PR, and 13 (54.2%) of no response. In 432 cases of complex cysts, CR was observed in 82 (19.0%), PR in 261 (60.4%) and no response in 89 (20.6%). The volume reductions in complex cysts with pre-treatment volume larger than 15 mL were higher than those of groups with smaller volumes (p<0.001). Pre-treatment volumes were not correlated with post-treatment volumes, nor with volume reductions. Volume reductions were not correlated with the amounts of injected ethanol. Mild and transient complications were observed in 41 cases (9.0%) during PEI, consisting of transient neck pain (n=36, 7.9%), transient unilateral vocal cord palsy (n=3, 0.7%), intracavitary hemorrhage (n=1, 0.2%), and transient hypotension (n=1, 0.2%). CONCLUSION: Our data suggest that the efficacy of PEI on AFTN is temporary and does not usually induce long-term complete remissions. In complex cysts, however, PEI may have potential as an additive treatment modality to thyroid hormone suppressive therapy

- Effects of Glucocorticoid on Apoptosis of Human Bone Marrow Osteogenic Stromal Cells.
- Ha Young Kim, Duk Jae Kim, Si Yeol Lee, Jeong Soo Hong, Dong Kwan Kim, Ghi Su Kim
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2002;17(1):23-31. Published online February 1, 2002
- 964 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Osteoporosis is one of the most serious side effects of long-term glucocorticoid therapy, but the mechanism of glucocorticoid-induced bone loss remains poorly defined. Glucocorticoid induces decreased bone formation and death of isolated segments of bone (osteonecrosis) suggesting that glucocorticoid excess may affect the birth or death rate of bone cells and thereby reduce their numbers. It has been known that reduction in bone formation is due to reduced proliferation in osteoblast precursor cells and reduced matrix synthesis in mature osteoblast. Here, we present evidence for dexamethasone-induced apoptosis on human bone marrow stromal cells (hBMSC). To understand the mechanism of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis, we investigated the effects of glucocorticoid on primary cultured hBMSC. METHEODS: Treatment with dexamethasone at the concentration of 10-9 M for 3~5 days significantly decreased cleavage tetrazolium salt WST-1 level/concentration by mitochondrial dehydrogenase in viable cells. Greater decrease was observed with higher concentration of dexamethasone (10-7 M, and 10-5 M). Apoptosis was measured by annexin V binding/propidium iodide using fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS) analysis and nuclear morphology stained with the fluorescence dye, Hoechst 33342. RESULTS: The level/concentration of apoptotic hBMSC (annexin V positive / PI negative) was increased with 10-9 M dexamethasone (1.2% to 5.3%) and further increased with 10-7 M, and 10-5 M concentration (11.7% and 12.5%, respectively). The same result was observed with Hoechst 33342 staining. CONCLUSION: These results indicate that glucocorticoid induces apoptosis on osteoblast precursor cell, hBMSC, and may contribute to decrease bone formation

- Clinical Applications of 18-FDG PET in Recurred Differentiated Thyroid Cancer with Negative 131I Whole Body Scintigraphy: A Comparative Analysis with 99mTc-MIBI Scintigraphy.
- Jong Chul Won, Sung Jin Lee, Tae Yun Lee, Il Seong Nam-Goong, Sy Yeol Lee, Ha Young Kim, Jung Hee Han, Jin Sook Ryu, Dae Hyuk Moon, Il Min Ahn
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2001;16(4-5):481-493. Published online October 1, 2001
- 932 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
In patients with differentiated thyroid cancer treated by surgery and radioactive iodine ablation, serum thyroglobulin(Tg) and 131I whole body scan(WBS) are recognized as being the best cooperative indicators for detection of recurrence or metastasis. However, in some cases, 131I WBS shows no specific lesions despite elevated serum Tg. Therefore, 18-Fluorine-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography(PET) has emerged as a useful method for the detection of 131I WBS negative thyroid cancers. The aims of the present study are to evaluate the clinical usefulness of this technique in detection and to compare the results with 99mTc-MIBI scintigraphy(MIBI) in cases of final results being confirmed by histologic diagnosis and other imaging methods. METHODS: We conducted a retrospective analysis amon 131I WBS negative recurred papillary thyroid carcinoma patients(male: female ratio=9:22, median age=42 yr). FDG PET was performed in 28 patients and MIBI 28 patients, 25 of whom were common to both groups. All patients had histologically proven recurrence/metastasis and negative 131I WBS results but persistently elevated serum Tg levels. In each case overall clinical evaluations were performed including histology, cytology, thyroglobulin level, other imaging methods, posttherapy 131I WBS and subsequent clinical course, to allow comparison with the results of FDG PET. RESULTS: In 19 cases of patients with negative 131I WBS, proven recurrence/metastasis lesions were detected in FDG PET. Compared with MIBI, FDG PET was found to be superior in 8 cases(including 2 patients with distant metastases). No FDG-negative/MIBI-positive tumor was observed. One FDG PET negative and MIBI negative case was proven 3 months later to be metastatic cervical lymph nodes, Sensitivities were 94.7% in the FDG PET group and 52.6% in MIBI. Diagnostic accuracy of FDG PET was superior to that of MIBI(93% vs. 62%, respectively, p=0.003). CONCLUSION: Our results confirmed the clinical usefulness of FDG PET for detection of 131I negative differentiated thyroid cancers and suggested the value of FDG PET as an initial diagnostic step, rather than MIBI, in these cases.

- Effectiveness of Percutaneous Ethanol Injection in Benign Cold Thyroid Nodules: Five Years' Experience.
- Seong Jin Lee, Jung Hee Han, Ha Young Kim, Jong Chul Won, Sang Wook Kim, Ho Kyu Lee, Il Min Ahn
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 2001;16(2):210-220. Published online April 1, 2001
- 1,030 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Percutaneous ethanol injection therapy (PEI) which is performed with the guidance of ultrasonography has recently been used in patient who had benign cold thyroid nodules. We performed this study to analyze the long-term effects of PEI on benign cold thyroid nodules. METHOD: From September 1995 to September 2000, we treated 198 outpatients (12 men and 186 women, who had a mean age of 40.8 years, with a range of 15-71) who had benign cold thyroid nodules at the Asan Medical Center. The PEI was performed on 141 patients who had solitary nodules (SN) and on 57 patients who had prominent nodules or Questionable or typing error? multiple nodules (MN). All patients had fine needle aspirations (FNAs) at least twice which resulted in a diagnosis of the presence of a colloid nodule. Thyroid hormone was given to all patients along with TSH measurements. The thyroid hormone dose was titrated to correspond to TSH level of a low normal range. These patients were followed up for mean period of 37.6 months (range 18-60). Patients who were treated with PEI were classified into three groups according to their volume reduction: a complete response (CR, which was above 90% in volume reduction), a partial response (PR, which was a 50-89%) reduction and No Response (which was below 50% or an increased size) groups. RESULTS: The overall pre-treatment volumes of the nodules were 15.7+/-19.8 mL. The overall post-treatment volumes were 2.4+/-2.6 mL and consisted of volume reductions of 70.1+/-17.1%. The results of PEI for all of the patients were: a complete reduction (CR) in 34 cases (17.2%), a partial reduction (PR) in 142 cases (71.7%) and No Response in 22 patients (11.1%). In 141 patients in the SN group, in which there was a mean follow-up duration of 36.7+/-11.2 months, the volume reductions were 68.3+/-18.8%. CR was observed in 20 patients (14.2%), PR in 103 (73.0%) and No Response in 18 (12.8%). In twenty-two of the SN patients (22/141, 15.6%) we were able to discontinue the thyroid hormone suppressive therapy because those nodules had markedly decreased in volume after PEI without any further increase of nodule size during the follow-up period. In 57 patients in the MN group, over a mean follow-up durations of 37.1+/-11.4 months, the volume reductions were 74.3+/-12.1%. CR was observed in 14 patients (24.6%), PR in 39 (68.4%) and No Response occurred in 4 (7.0%). During the follow-up period after PEI, further volume reductions were observed for 36 months after thyroid hormone suppressive therapy in the Response Group. Differences in volume reductions between the SN and MN groups were not statistically significant but the volume reductions in patients who had a pre-treatment volume larger than 15 mL were higher than those in the smaller group (p<0.001). In the cases of the SN and MN groups, volume reductions did not correlate with either the amount of injected ethanol or the pre-treatment volumes, but the pre-treatment volumes correlated with post-treatment volumes in the patients who had SN (p<0.001, r=0.411) and MN (p<0.001, r=0.729). We observed mild, but transient complications in 32 patients (16.2%) during PEI which included a transient neck pain (n=27, 13.6%), a transient unilateral vocal cord palsy (n=4, 2.0%), and an abscess formation (n=1, 0.5%) which was cured. CONCLUSION: These results suggest that PEI is a feasible adjunctive therapy to use in thyroid hormone suppressive therapy for benign cold thyroid nodules


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



